Problem
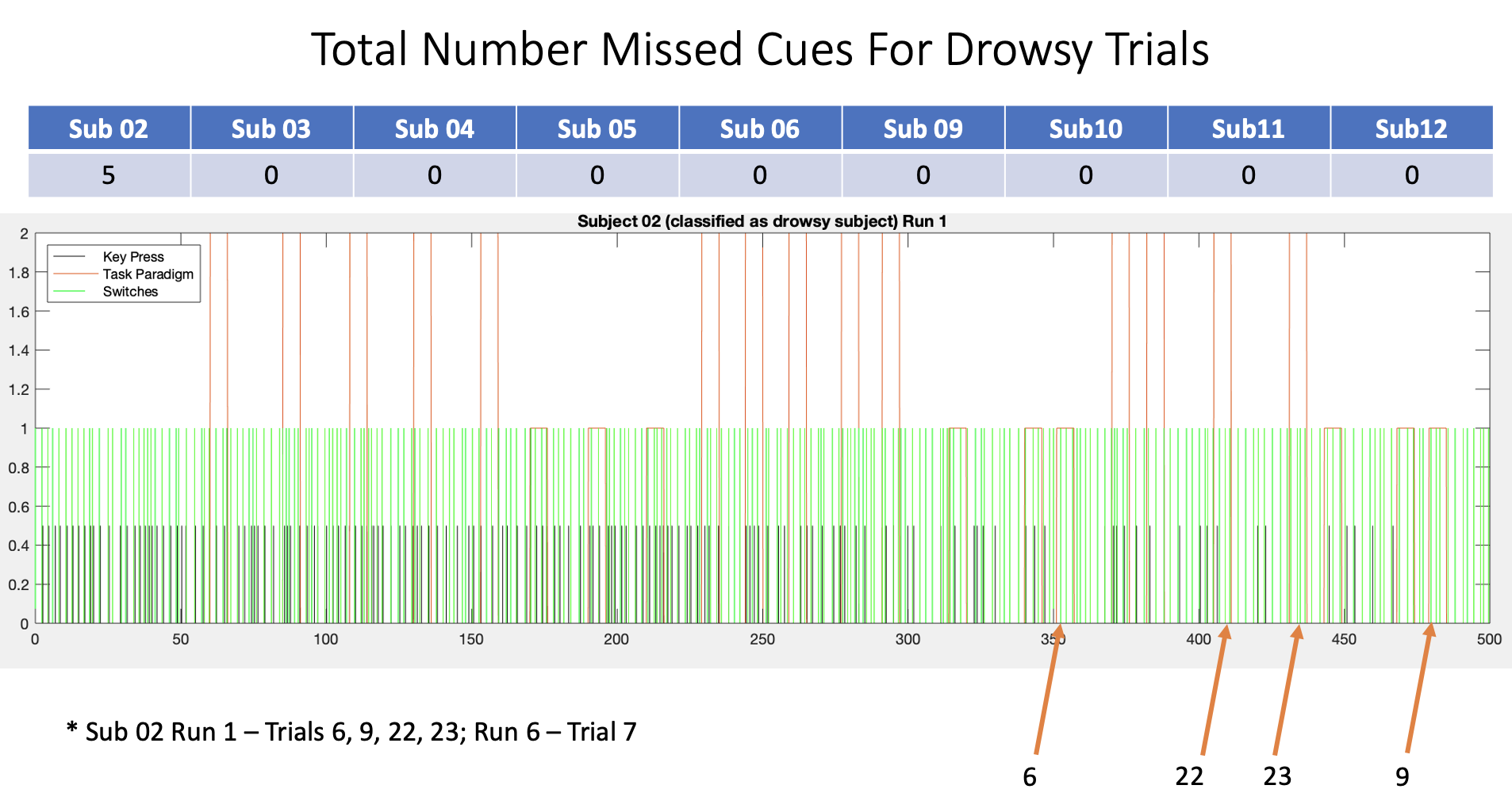
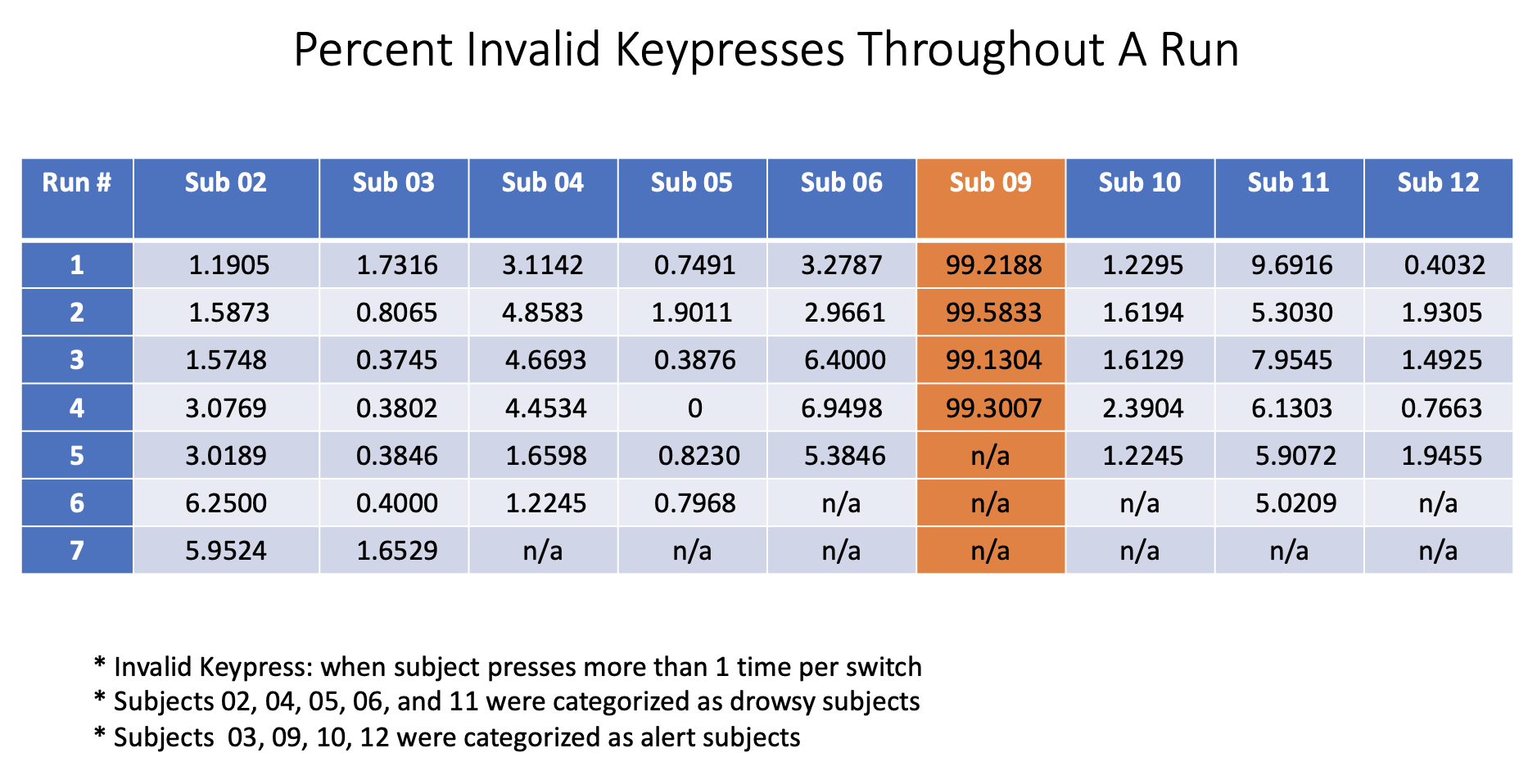
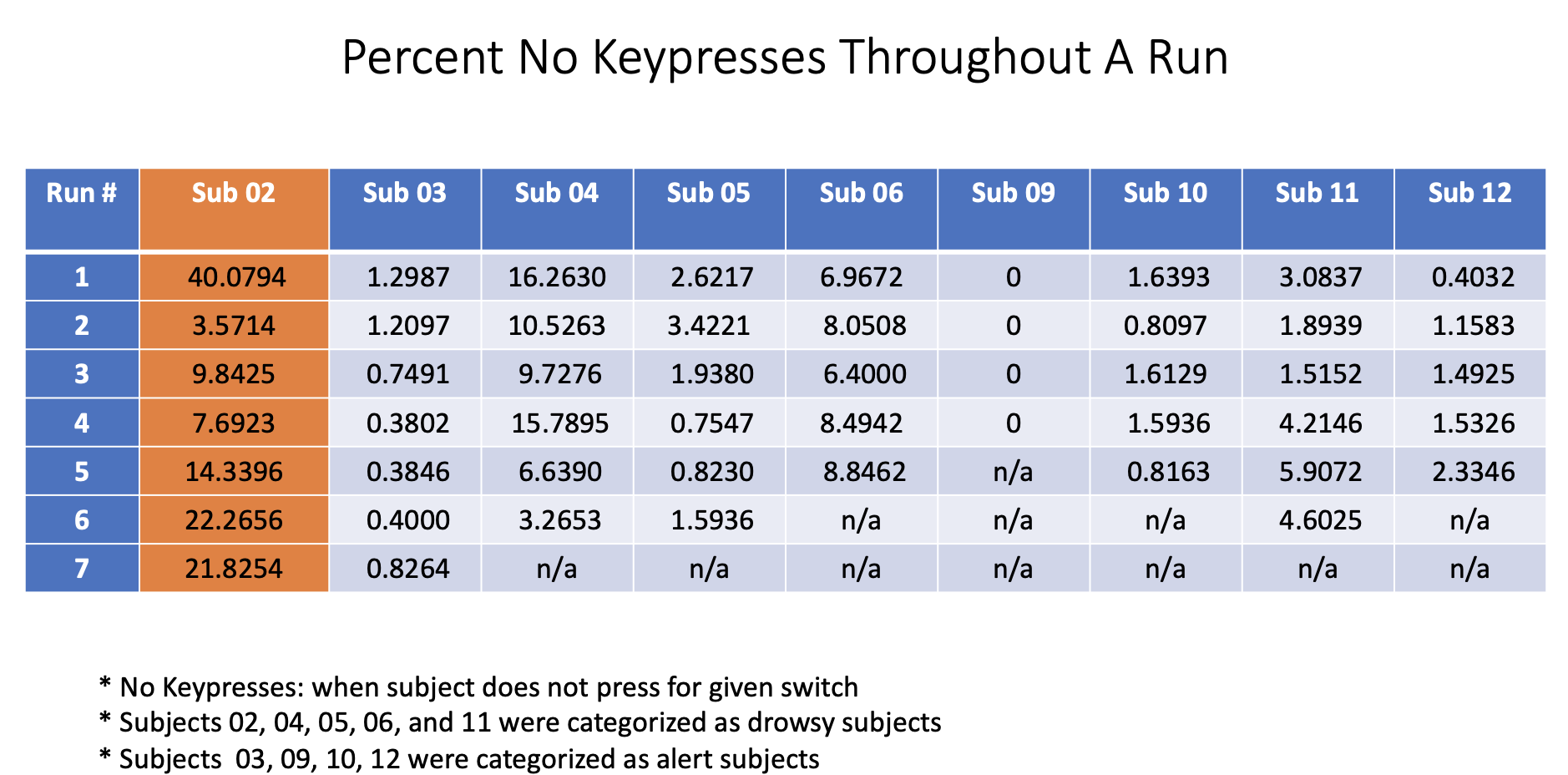
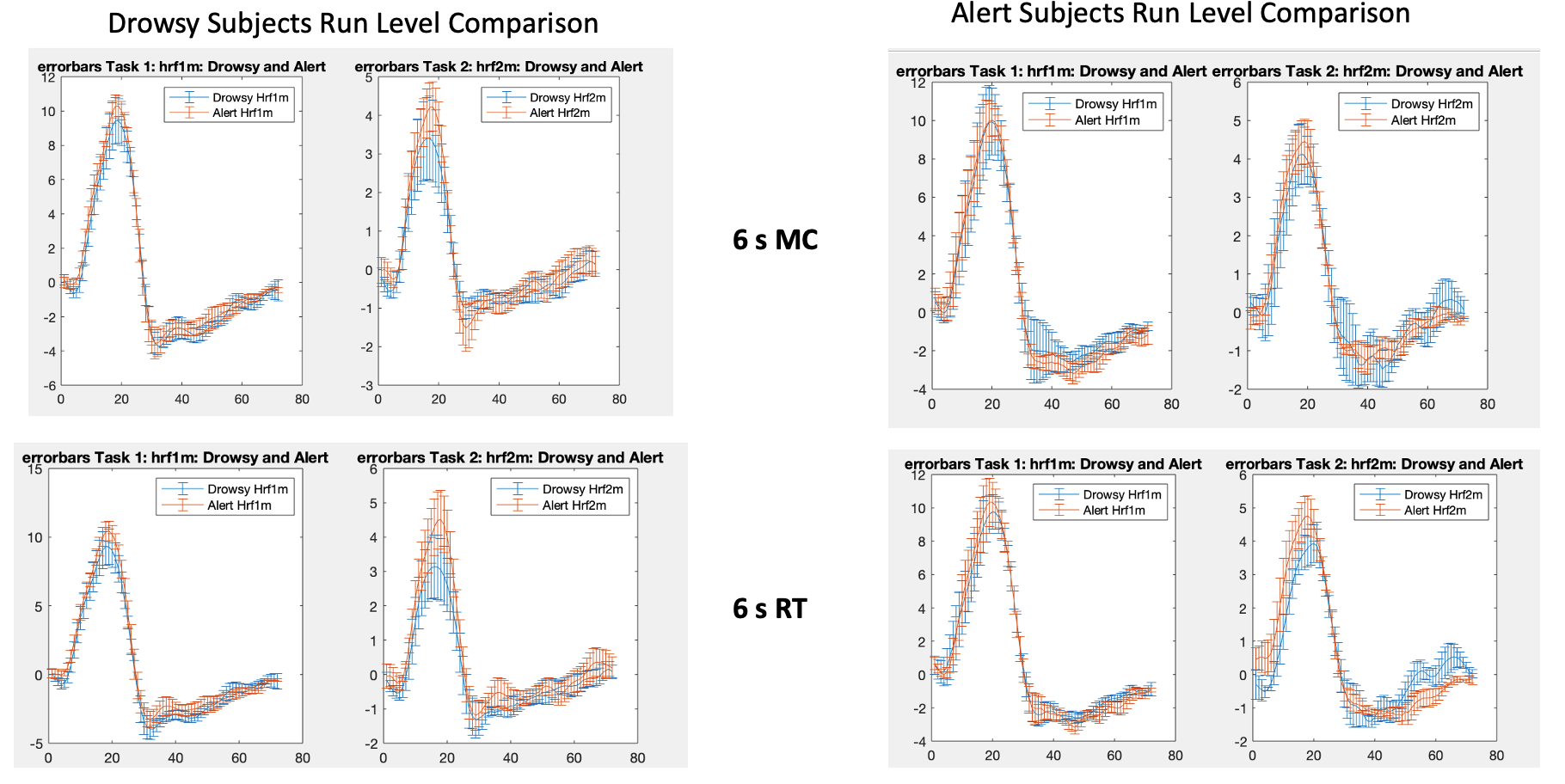
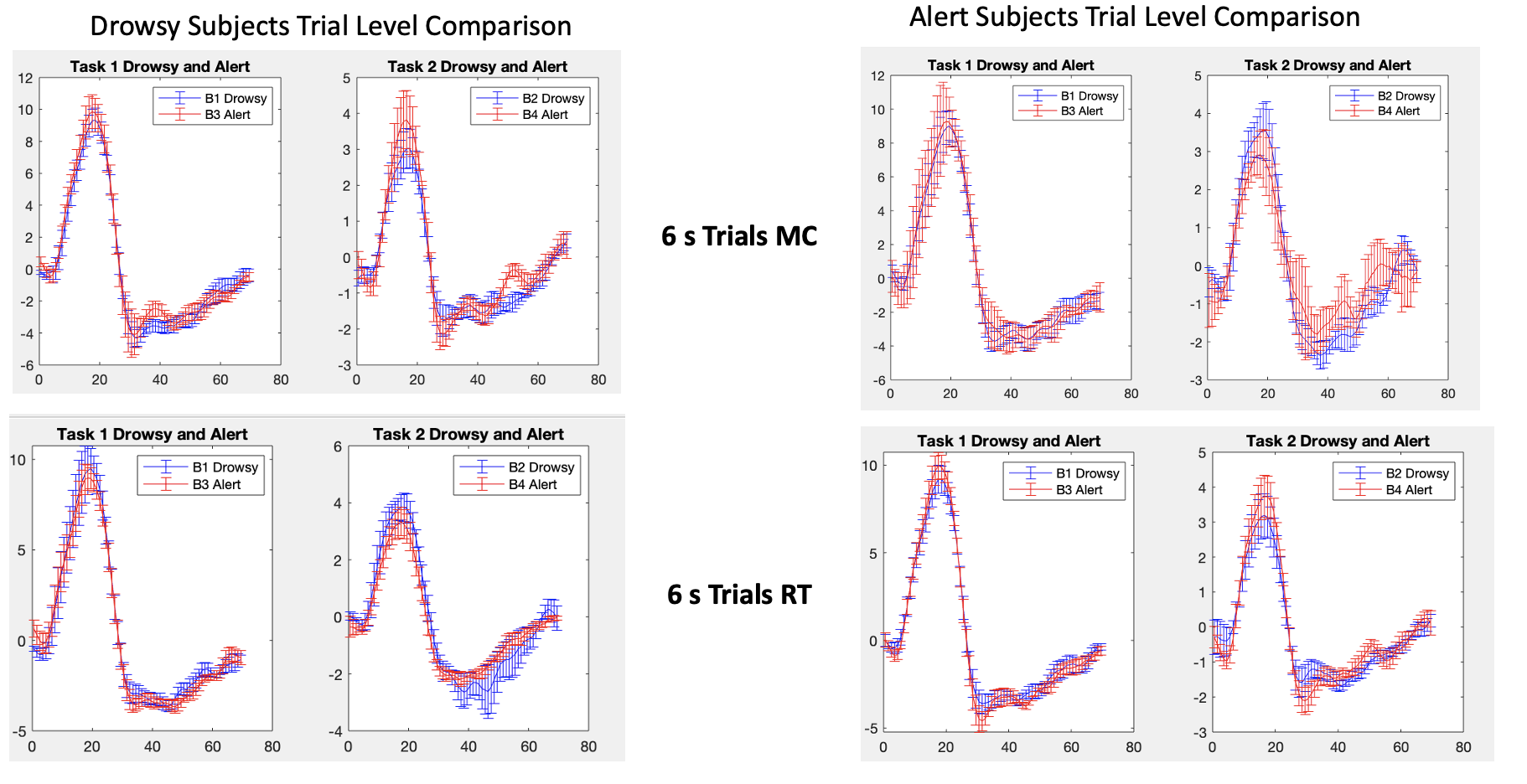
This was one of the projects of my first co-op at Massachusetts General Hospital's Martinos Center for Biomedical Imaging. Most often, MRI scans can take upwards of an hour. In that time, it is easy for a person to become drowsy. There had not yet been data and analysis on if there is a difference in hemodynamic response functions between those "drowsy" subjects and more "alert" subjects.
Objective
To characterize arousal modulations shown in the hemodyanmic response function (HRF) in "drowsy" and "alert" subjects.
Skills Employed
- MATLAB
- Linux environment